Kano model: what it is and how to use it for maximum customer satisfaction
Learn how the Kano model can be used to prioritize product features.

Product feature development is an exciting time for your entire team. Everyone has ideas they think will be the most desirable, from first concepts to production to marketing. With all that incredible enthusiasm, how do you decide what features to run with and which ones are better left behind? Which features should you prioritize, and which should you wait on?
Determining what product features make sense practically and financially can delay your product launch and even lead to financial loss and customer loyalty erosion if you choose incorrectly. That’s where the Kano model comes into play. The Kano model can enhance your products by prioritizing development efforts based on customer feedback.
What is the Kano model, and why is it important?
The Kano model is an analysis framework used to prioritize product features according to the degree to which they will likely satisfy customers.
A Kano analysis helps product teams prioritize where to allocate resources more effectively, saving time and budget while increasing potential revenue.
Dr. Noriaki Kano, a Tokyo University of Science professor, developed the Kano method in the 1980s. His research shows that customer satisfaction with product features depends on the level of their functionality. He found that features can be classified into five categories, and you can determine potential customer reactions with a survey.
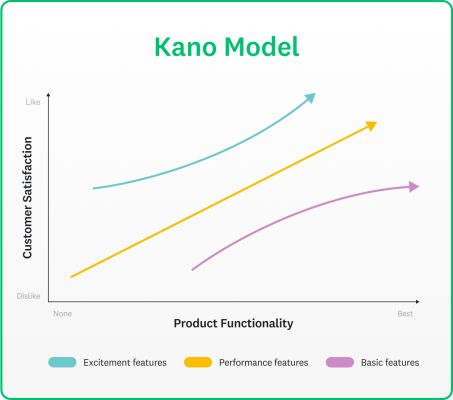
Kano model feature categories
The Kano model assigns product features to five categories:
- Must-have or must-be (basic features)
- Performance (one-dimensional)
- Attractive or delighters (excitement)
- Indifferent (irrelevant)
- Reverse (unwanted)
You should strive to provide must-have, performance, and attractive features and avoid indifferent and reverse features.
Must-have features
Product features that customers expect fall into the must-have feature category. If your product doesn’t have these basic features, it will be considered incomplete or unacceptable.
Must-have features are needed and expected, but having them won’t increase customer satisfaction or cause dissatisfaction (though not having them causes dissatisfaction). These basic features need to be there, or the product will fail.
Must-have feature examples:
- Brakes on a car
- A bed in a hotel room
- A cell phone that makes calls
Performance features
The performance category includes add-ons customers want. These features add to customer enjoyment of the product.
Lots of performance features typically mean increased customer delight and customer loyalty. They are considered one-directional because they increase satisfaction and functionality.
Performance feature examples:
- Multiple payment methods for food delivery
- Great gas mileage
- A thermos handle
Attractive features
Customers don’t necessarily think of “delightful” features. Typically, they want incrementally better versions of the same products.
The Kano model can show how innovation and fresh features would be perceived. This technique can help a company get a leg up over the competition if they determine customers would perceive a new feature to be new and special.
In some cases, delightful features can become expected basic or performance features over time.
Attractive feature examples:
- Heated car seats
- Flashlights on phones
- Webcams on laptops
Indifferent features
These features don’t affect customer delight and satisfaction either way. They are unimportant or irrelevant to the customer.
Indifferent feature examples:
- The brand of rug in your hotel room
- Phones with several color options
- Multiple smartphone ringtone options
Reverse features
Reverse, or negative features, are aspects that directly decrease satisfaction and happiness. Keep in mind that reverse features may be inconvenient for some customers or in some situations but not others.
Reverse feature examples:
- Waiting for a server to seat you at a diner
- Very limited menu at a restaurant
- Graphic-only instruction manual for assembling a table
How does the Kano model work?
Kano analysis determines customer satisfaction with a feature.
The features are plotted on a Kano evaluation chart. Depending on where they fall on the chart, a company can visualize a product feature’s importance, customers’ expectations for it, and customer delight.
Consider this real-world Kano model example:
Your product team can increase satisfaction by prioritizing product features (new and updated) that customers want and avoiding features that detract from the user experience.
In a car, some features are basic and functional, such as must-have features like brakes. Automatic car brakes aren’t basic but are functional and improve the driving experience, which may satisfy and attract your target customer.
The Kano model can give you a business case for prioritizing automatic brakes over extras like interior LED lights that customers don’t want or need.
Benefits of using the Kano model
The Kano model can enrich your product development process and help achieve the following outcomes.
- Save time and resources. Rather than moving forward with features you think will satisfy customers, use a Kano analysis to make data-driven decisions. This saves time, effort, and money in the long run.
- Group your best features. Use your Kano analysis to develop a plan to both enhance performance and increase customer satisfaction with features according to customer preferences.
- Prioritize development efforts. Find out what features need immediate attention to improve performance and prioritize those fixes before approaching new features.
- Improve customer satisfaction. Please customers faster by fixing broken features or shoring up basic features that delight customers, improve customer satisfaction, and increase revenue.
When to use the Kano model
The Kano model is an efficient method but has specific use cases. Here's when to use the Kano model.
- Develop a data-driven product roadmap. Kano analysis can direct your roadmap, helping you prioritize product feature updates and new features. Ultimately, you can direct resources to areas that will have a return on investment.
- Competitive analysis. Employ the Kano model to benchmark your product or service against competitors. By understanding the must-have, performance, and delighter features in your industry, you can identify areas for differentiation and innovation.
- Customer segmentation. When targeting different customer segments, the Kano model can help tailor offerings to meet varying expectations across target audiences. Understanding how different groups perceive product features allows for more effective marketing and product strategies.
How to create a Kano model survey
1. Define your objectives
Are you aiming to learn which current product features to update first? Do you seek insights to prioritize new, exciting features? Or is it a mixture of both?
Establishing clear and detailed objectives will serve as a foundational guide to your research. For example, if your objective is to prioritize new product features that you identified through prior concept testing, it’s not an optimal use of time to survey current features.
2. Identify features to evaluate
Identify 15 to 20 features or attributes that you wish to evaluate. Ensure the features align closely with your business objectives and the product team can plausibly implement them.
Using the Kano model, you will be able to determine whether to allocate resources to develop these features. You’ll also learn if customers would be excited by the features or simply expect them to be there.
3. Design the Kano model survey
The Kano model comes with standardized, preset questions, like a Net Promoter Score® survey.
Kano survey questions:
- If you had (proposed feature), how would you feel? (Functional question)
- If you didn’t have (proposed feature), how would you feel? (Dysfunctional question)
The rating scale responses range from "I like it" to "I dislike it."
In the survey, list each feature separately so as to not confuse the respondent.
4. Select your target audience
To identify and recruit participants, consider your target customer. Not all customers will use a specific product feature, so it’s important to find that the feature you are testing is relevant to the target audience.
This may involve current customers who regularly interact with your product or service and potential customers who have shown interest but haven’t yet converted.
5. Analyze the results
Organize your survey responses based on the two functional and dysfunctional questions asked—“If you had (proposed feature), how would you feel?” and “If you didn’t have (proposed feature), how would you feel?”.
Both questions are answered on a five-point rating scale:
- I like it
- I expect it
- I’m neutral
- I can tolerate it
- I dislike it
You will plot your responses on a Kano evaluation chart. Based on the chart, you will learn if the feature is a must-have, one-dimensional, attractive, indifferent, or reverse.
For example, if respondents overwhelmingly responded that they expected an ergonomic water bottle design and would dislike the absence of the product feature, the feature would be considered a must-have.
This information would help product teams prioritize the development of an ergonomic water bottle handle design over lower-rated features, like a themed colorway.
6. Prioritize features
Prioritize the features that are most likely to enhance customer satisfaction. Focus on implementing features that align with your business goals and resources, with a clearer data-driven prioritization showing how features will likely be perceived by customers.
Best practices for Kano analysis
Kano analysis is an invaluable tool. They direct your product roadmap and optimize resources—when the Kano analysis is conducted correctly. Keep these best practices in mind as you perform your next Kano analysis.
- Choose the right features to test. Aim to test between 15 and 20 features to ensure that the analysis remains manageable and delivers actionable insights. This targeted approach helps prevent survey fatigue among participants.
- Select a representative sample. This means identifying a sample that aligns with your target audience.
- Combine with qualitative research. Qualitative surveys will delve deeper into the participants' feelings, motivations, and experiences related to the features evaluated in the Kano survey.
Limitations of the Kano model
As with any method, there are some limitations to the Kano method. Consider the following Kano model disadvantages to make an informed decision about proceeding (or not) with the Kano model:
- Subjectivity in categorization. The process of categorizing features into different Kano model classifications is not standardized and can be highly subjective. Stakeholders may interpret customer responses differently, leading to inconsistent outcomes.
- Changing customer expectations. Customer preferences can change due to trends, market conditions, or technology advances.
- Context-dependency. The Kano model focuses on customer satisfaction in relation to specific product features. It may overlook other critical factors affecting customer satisfaction, such as brand reputation, price sensitivity, or user experience like conjoint analysis.
- Requires follow-up research. Kano analysis is a quick and efficient way to sort features, but it usually requires follow-up research to refine decision making.
- Confusing implementation. The rating scales are ordinal at best, so analysis is limited.
Improve feature development with SurveyMonkey
The Kano model is a tool to evaluate feature prioritization. It helps product teams understand which features need attention and how new product features fit into your workflow to best satisfy customers.
That said, you can use many tools to measure, track, and improve customer satisfaction. SurveyMonkey survey templates are written by survey experts to expedite the survey creation process, saving you time and resources.
Market research product surveys and software evaluation surveys can help you ensure product feature refinements identified by the Kano model meet customer expectations.
Customer satisfaction surveys and Net Promoter Score surveys are standard customer experience surveys that monitor the overall health of a business and can track the efficacy of Kano model decisions.
In addition to customer experience surveys, you can use brand tracking survey templates to monitor the health and perception of your brand and products. Drastic changes may help you identify that features need to be updated—and the Kano model can help you prioritize those features.
Get started with our market research services to understand usage and attitudes towards your product, including market research surveys and product concept analysis today.
Net Promoter, Net Promoter Score, and NPS are trademarks of Satmetrix Systems, Inc., Bain & Company, Inc., and Fred Reichheld.